This article by Impact Solutions shows the ADR/RID Test Requirements and Model Liquids Test Procedure, Compatibility Testing and a Case Study: Container ESCR Performance.
ADR/RID Test Requirements and Standard Liquids
UN Transport of Dangerous Goods Model Regulations, Paragraph 6.1.5.6.
This test is only required for plastic containers.
If the product to be carried is modelled by a ADR model liquid then the container is conditioned with the standard liquid for 21 days at 40°C.
If the product is not modelled by a ADR model liquid then the container is conditioned with the product for 6 months at ambient.
Following conditioning the container undergoes the performance tests of air leakage, internal pressure, drop impact and stack test. The conditioning medium is used only for the stack tests.
| Model Liquid | Action | Comment |
| Water | None | No Conditioning Required |
| Wetting Solution | Stress Cracking | <1% liquidabsorption 1 to 10% detergent Solution |
| Butyl Acetate | Slight Stress Crack | <4% liquidabsorption |
| White Spirit | Softening | <7% liquidabsorption |
| Acetic Acid | Mild Stress Crack | ~1% absorption |
| 55% Nitric Acid | Oxidation, embrittlement | |
Compatibility Testing
Compatibility tests are used to compare the effect of chemical products on polyethylene against the effects of ADR/RID standard liquids. These tests can be used to reduce the amount of ADR/RID testing required on containers. They measure the following properties:
Absorption using sample immersion for 28 days at 40°C to compare weight uptake of the product to that of white spirit or butyl acetate.
Molecular degradation using melt flow index measurements to compare the level of degradation caused by sample immersion in the product for 28 days at 40°C with that of nitric acid.
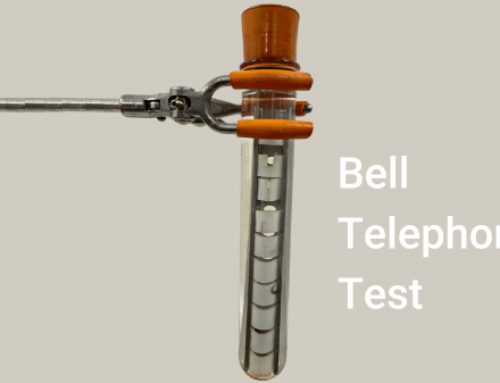
ESCR using the Bell Telephone Test (ASTM 1693) to compare the stress cracking nature of the product with a wetting agent (detergent solution).
Case Study: Container ESCR Performance
There are two approaches that are taken by IMPACT Solutions to assess the suitability of containers for the long term handling of chemicals (model liquids) with respect to stress crack performance.
Accelerated stress crack tests can be performed on containers using an appropriate environmental medium and applying an overload to the stack test. In general, this is performed using a wetting agent and either a specified higher SG or a fixed stacking load, e.g. 500kg loads for 25-litre containers.
In such cases, environmental stress cracking resistance (ESCR) failure takes place at stress concentrations promoted by the higher stack load. For example, in the overload stacking of 200-litre drums, failures occur around the inside of the drum base resulting from the high tensile stresses on the inner drum wall at these points.
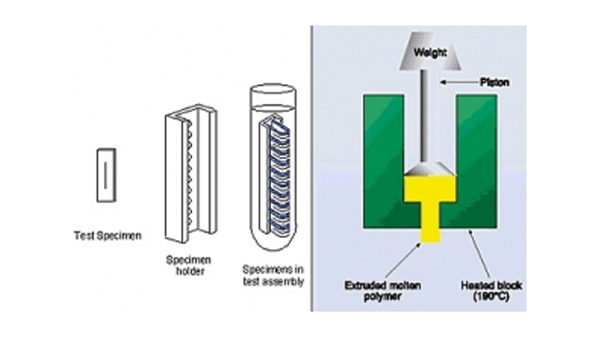
An alternative approach taken by IMPACT Laboratories is to assess the ESCR of the drum wall material using laboratory tests such as the Bell telephone test (BTT) or the full notch creep test (FNCT). The FNCT, in particular, has been shown to correlate well with the performance of accelerated container stack tests (see below) and can provide a rapid means of evaluating container performance. This involves removing and remoulding material from the container wall and performing the FNCT in accordance with ISO 16770.
To learn more about how Impact Solutions can help you with your testing requirements, please contact a member of our team.